MASTER ADVANCED PHYSICS
(For all Top Exams)
Video – 2
KINEMATICS – 2
Acceleration –
Change in velocity
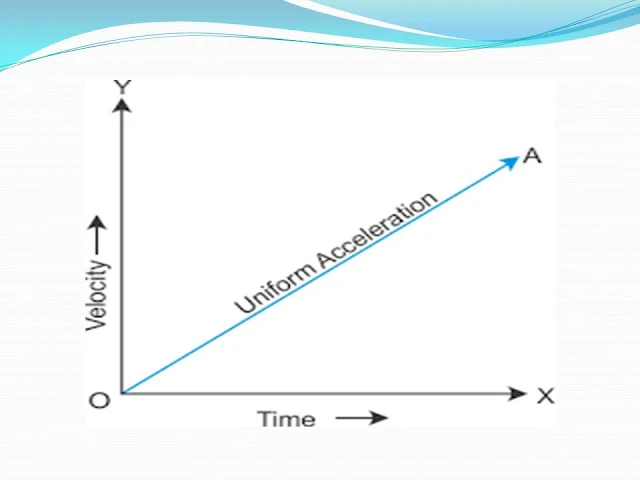
Uniform acceleration
Rate of change in velocity is constant
Change in Velocity in one second.
V= 0 t= 0
V= 10 t= 1
V= 20 t= 2
V= 30 t=3
A = 10m/s /s
Equations of motion for uniformly accelerating body
U, v, a, S, t
V – u / t = a or v = u + at
S = ut + ½ a t*t
V2 – u2 = 2as
Derivation of the three equations
V= u + at is by definition true
(U + v) / 2 = average velocity = s / t
Ut + vt = 2s
Ut + (U + at)t = 2s
Ut + ut + at 2 = 2s
Dividing by 2
S = ut + ½ at2
With the first two equations we can get
V2 – u2 = 2as
by simple substitution
Displacement – time graph for uniformly accelerated motion
Graph – parabola
Graph – slanted straight line